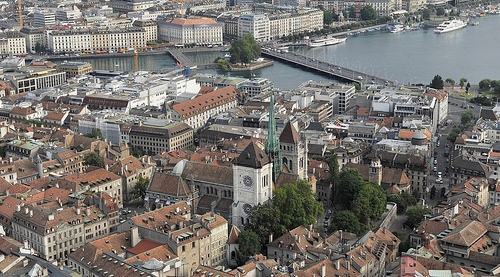
Geneva (French Genève, Italian Ginevra, raw Genevra, English
Geneva) is the capital of the canton of Geneva of the same name.
The city lies directly on Lac Léman (German Lake Geneva) and on
the Rhone. One of the most well-known sights next to the seaport
is the Jet d'eau, a water fountain up to 140 m high, and the
historic old town situated on a hill. Geneva is home to around
200 international institutions, including the United Nations'
second headquarters (next to New York City), and
non-governmental organizations. For this reason, the city
accommodates many foreigners and has an international
atmosphere, which is also reflected, for example, in the
high-quality gastronomy.
Geneva is the capital of the
canton of the same name, which is the westernmost canton of
Switzerland. The city lies at the outflow of the Rhone from Lake
Geneva. The city is the second largest in Switzerland and is
also considered to be the most cosmopolitan in Switzerland. It
is partly due to the fact that John Calvin, a reformer and the
founder of Calvinism, lived and worked here. The city was an
important university city early on. The first general of the
Swiss army, Guillaume-Henri Dufour, also comes from Geneva, as
does the initiator and founder of the International Committee of
the Red Cross, Henry Dunant. Since four of the five founding
members of the Red Cross are from Geneva, it is not surprising
that this organization has its headquarters here.
When
the League of Nations was founded in 1919, Geneva was chosen as
its seat. Although Switzerland did not join the United Nations
(UN) after the Second World War – this only happened in 2002 –
Geneva became the second most important seat for the UN. The
United Nations Office at Geneva (UNOG) is located here. This
could continue to use the buildings of the former League of
Nations. In neutral Switzerland, it was much easier to bring
conflicting parties to the table for negotiations. Although the
UN's power-political organs are less located in Geneva, the UN
Human Rights Council has its headquarters here. The World Trade
Organization (WTO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) also
have their headquarters in Geneva.
In addition to the
university, the European Center for Nuclear Research (Conseil
Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire CERN) is worth mentioning.
The world's largest research center in the field of particle
physics operates several connected particle accelerators
north-west of the city on both Swiss and French soil. At 27
kilometers long, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the largest
machine in the world.
Northwest of Geneva lies the Jura.
By plane
The city has the medium-sized Geneva International
Airport (IATA: GVA) . It is a few kilometers northwest of the city
center and has numerous inner-European city and holiday connections
as well as a handful of long-haul flights.
As of 2022, there
are direct flights to Geneva from German-speaking countries from
Berlin (easyJet), Düsseldorf (Eurowings), Frankfurt, Munich (each
Lufthansa and SWISS) and Vienna (Austrian).
A flight within
Switzerland to Geneva is only offered from Zurich (with SWISS),
whereby the connection by train only takes about 2:40 hours. Basel
and Bern are also connected by rail at frequent intervals. The SBB
timetable can be accessed online.
In addition to the
terminal, the airport has its own underground SBB long-distance
train station, with all trains starting and ending here running via
Geneva main station - the journey takes about 7 minutes, during the
day there is a train every 15-20 minutes at the latest. There are
both German-language ticket machines and an SBB customer center. In
Switzerland there are no tariff differences between train types, so
you can board any train (IC and IR) towards Geneva with a ticket
bought there.
By train
Geneva's main train station, Gare
Genève Cornavin, is in the immediate vicinity of the (historical)
center of the city and has frequent and very reliable domestic
connections as well as regular international connections to Paris
(with the TGV Lyria) and Milan (EC of the SBB). It is also a hub for
regional trains, trams and buses. In addition to a large SBB
customer center, there are numerous ticket machines, including
German-speaking ones, and some shops that are also open on Sundays,
including two supermarkets.
All connections can be queried in
the SBB electronic timetable and via their app.
In the street
Geneva is on the A1, Switzerland's main motorway. Near Geneva, in
the south-west of the city, there is a motorway junction where
several motorways intersect: the N1 from Lausanne intersects with
the E62 to Lyon (130km) and the E25 to Chamonix in the south-east.
By bicycle
Rhone route
By boat
Geneva is located on
Lac Léman and can be reached by boat.
The city and agglomeration of Geneva has a dense public transport
network. The city is well served by Geneva Public Transport's trams
and buses. The agglomeration and surrounding towns can be reached by
S-Bahn. The connections are listed in the electronic timetable.
The Léman Express network connects the main Geneva train
stations with 18 French cities in the region.
There is a
network of good hiking trails in the nearby Jura. The Jura Höhenweg
leads to the highest mountains in the Jura Mountains, which offer
beautiful vantage points.
Probably the most famous sight in Geneva is the Jet d'eau wikipediacommons right next to the port, a water fountain up to 140m high (open all year round except November, as well as at night and in strong winds). Also known are the research center CERN and the headquarters of the United Nations. But Lake Geneva shouldn't be missed either, as well as the historic old town.
St. Peter's Cathedral
Temple de la Fusteria, Place de la Fusteria
18, 1204 Geneva
American Church
Eglise Note Dame, Place de
Cornavin, 1201 Geneva .
Church of the Madeleine
St Joseph
St.
Clotilde
Temple de Autitoire
Russian Church (Eglise Russe),
Rue Toepffer 9, 1206 Geneva.
Temple de Saint Pierre. The Cathedral of
St. Peter (Temple de Saint-Pierre) is located on the top of the Old Town
hill. From 1160 to 1232 the bishop's church was built in the
Romanesque-Gothic style, after which it was remodeled several times. In
their place were Roman temples and, since the 4th/5th century, Christian
basilicas. The two main towers were not completed in the 13th century.
The metal spire above the crossing dates from 1895 and replaced the
15th-century bell tower that had burned down. The portico from 1756 with
its six Corinthian columns is a real break in style and does not match
the building. A staircase with 157 steps leads to the north tower. The
64 meter long interior impresses with its balanced proportions. It was
cleared out on the occasion of the Reformation and therefore does not
have any large decorations, as is desired in a Calvinist church.
However, there are a number of tombs and tombstones in the church. The
three-aisled nave ends in a narrow transept with a semicircular choir.
The organ from 1965 with 6000 pipes is located in the large gallery
above the portal. The stained glass windows in the choir are copies of
the 15th-century originals housed in the Musée d'Art et d'Historie.
Below the church is one of the largest archaeological excavation sites
in Europe. The archeology site is open Tues – Sun, see International
Museum of the Reformation.
Castles, palaces and castles
Palace
of Nations. The European headquarters of the UN. With an area of
25,000m², it is the second largest complex in Europe after the Palace of
Versailles.
Hôtel de Ville, Rue de l'Hôtel-de-Ville 2. City Hall.
Old Arsenal.
A granary built in 1588/1634, which was used as an arsenal of weapons
until 1877. Today it houses the State Archives of the Canton of Geneva.
Palais Eynard, Rue de la Croix-Rouge 4, 1204 Geneva. The palace (1821)
is used by the city for representation.
Palais Athénée, Rue de
l'Athénée 2, 1205 Genève commons. The Palais (1826) houses an art
gallery.
Headquarters of the World Trade Organization WHO from 1926.
Headquarters of the International Red Cross
The WMO (Word
Meteorological Organization) building designed as a glass ship from
1999.
Villa Bartholoni
Reformation Monument . The monument is over 100 meters long. It is
located south-east of the Place de Neuve on the wall under the
Promenaden de la Treille.
Monument National. The Monument National is
a monument from 1869 and commemorates the incorporation of Geneva into
the Swiss Confederation in 1815. It is located in the English Garden.
International Museum of the Reformation, Rue du Cloître 2, 1204
Genève (bus 36 Cathédrale stop/ bus 2, 7, 12, 16, 20, Molard stop).
Tel.: +41 (0)22 310 24 31, fax: +41 22 310 74 45, e-mail:
info@musee-reforme.ch. History of the Reformation initiated by Jean
Calvin. With the help of books, manuscripts, pictures, engravings,
various utensils and the latest audio-visual means, the adventure of
this movement that started in Geneva in the 16th century and became one
of the great families of Christianity is presented. The museum is
located on the Cour Saint-Pierre, in the magnificent Maison Mallet,
built in the 18th century on the site of the former monastery of
Saint-Pierre, where the Reformation was welcomed in 1536. The museum is
connected underground to the archaeological site under the Saint-Pierre
Cathedral. Together with these cities, the cathedral and its towers, it
becomes a new cultural offer in Geneva, the Espace Saint-Pierre. CHF 10
adults ("AHV/ IV/ unemployed/ students aged 16-25/ apprentices CHF 7,
young people aged 7-16/ adults in groups of 15 or more (accompanying
person free) CHF 5, children under 7 years/ members of the IMR
association free "). Guided tours on request. Open: Tue – Sun 10 a.m. –
5 p.m., 24.12., 25.12., 31.12. + 1.1. closed; Easter Monday, Whit Monday
and Federal Day of Thanksgiving, Repentance and Prayer open. Wheelchair
accessible.
Musée d'Art et d'History, Rue Charles-Galland 2, 1206
Geneva. Phone: +41 (0)22 418 26 00 . Museum of Art and History. Feature:
Photographing allowed. Open: 11am-6pm, Monday closed.
Casemates
(Cabinet d'arts graphiques), Promenade du Pin 5. Email: mah@ville-ge.ch.
Open: 11am-6pm, closed Mondays.
Natural History Museum (Muséum
d'histoire naturelle de la Ville de Genève), Route de Malagnou 1 . Open:
10am-5pm, closed Mon.
Ethnographic Museum (Musée d'ethnographie de
Genève), Boulvard Calr-Vagt 65 . Open: 11am-6pm, closed Mondays. Price:
permanent exhibition free of charge.
Patek Philippe Museum, 7 rue des
Vieux-Grenadiers. Clock and Enamel Museum. Open: 2-6 p.m., closed on Sun
and Mon. Price: 10 CHF, children free.
Museum of Modern and
Contemporary Art (Musée d'Art Moderne et Contemporain, MAMCO), 10 rue
des Vieux-Grenadiers. Open: Tue - Fri 12pm - 6pm, Sat + Sun 10am - 6pm.
International Red Cross and Red Crescent Museum (Musée international de
la Croix-Rouge et du Croissant-Rouge), Av. de la Paix 17, 1202 Geneva.
Phone: +41 (0)22 748 95 11 . Open: Tue-Sun: April to October 10 a.m. to
6 p.m., November to March until 5 p.m.
English Garden, Quai Général Guisan.
Botanical Garden, 1, ch. of
the Empress
Geneve Plage, Quai de Cologny 5 Port-Noir 1223 Geneva. An inner-city
outdoor pool right on the lake, with many swimming and sports
facilities. Open: daily 9.00 a.m. - 8.30 p.m. Price: Children from 6 to
15 years: 3.50 adults (from 16 years): 7. Adults from 5 p.m.: 4.50.
In June 2008, Geneva was the venue for UEFA EURO 2008.
Like the rest of Switzerland, Geneva is known for its high-quality
but by no means cheap cuisine. A single main course quickly costs
between 20 and over 50 Sfr. The city offers a variety of small
brasseries and large gourmet temples with many international influences,
often accompanied by excellent wines.
The longeole is a
traditional raw pork sausage with a protected designation of origin. The
difference to other sausages are the fennel seeds and the rind, which
must not be missing in the sausage. The raw sausage must be cooked
between 2 and 3 hours at around 70°C to soften the rind. The Geneva
specialty is usually served with artichoke or potato gratin, but potato
or carrot salad is also an option.
Cheap
Cheap food in Geneva
is limited to street food and supermarkets, and even here the prices are
already above the level in Germany or Austria. There is a rich selection
of oriental specialties in particular, but grilled chicken is also
widespread (in a sandwich approx. 10 Sfr.). The widespread supermarket
chains Migros and Coop offer a variety of sandwiches and salads (from
around 5 Sfr.).
As expected, the large number of international guests in combination
with the already high price level also has an impact on the overnight
prices. Even simple hotels are rarely less than 100 Sfr. to get per
night. There are a handful of downtown hostels, as well as several
airport hotels that are often competitively priced. On the other hand,
one luxury hotel after the other is lined up around the shore of Lake
Geneva in the city center. Find out in advance if there are important
conferences in the city (eg the UN) or an event at the Palexpo
exhibition center - prices skyrocket months in advance.
Upscale
Hôtel Beau Rivage, Quai du Mont Blanc 13, CH 1201 Geneva. Phone: +41
(0)22 716 66 66, email: reservation@beau-rivage.ch.
Tickets for the public telephone booths can be bought at the kiosk.
Drinking water fountains can be found all over the city, with which
you can greatly reduce the cost of drinks on the go.
foreign
representations
Consulate General of the Federal Republic of Germany,
Consulate Général de la République fédérale d'Allemagne, Case postale
171, 1211 Genève 19. Tel.: +41 22 730 11 11, Fax: +41 22 730 30 43.
Location and special features
Geneva lies between
the Pre-Alps and the Jura. The Mont Salève in the south of the city is
considered to be their local mountain, but it is already on French
territory. The city area is 15.89 square kilometers.
The annual mean temperature for the normal period from
1991 to 2020 is 11.0 degrees Celsius, with the coldest monthly mean
temperatures being measured in January at 2.1 degrees Celsius and the
warmest in July at 20.6 degrees Celsius. On average, around 73 frost
days and 7 ice days can be expected here. There are around 64 summer
days on average over the year, while there are usually 17 to 18 hot
days. The MeteoSwiss weather station is 411 m above sea level. M. at
Geneva Airport, about 6 kilometers from the city center (as the crow
flies).
The highest temperature ever measured in Geneva was 39.7
degrees Celsius (July 7, 2015). This is also the highest value ever
measured on the north side of the Alps. The maximum value for the
average duration of sunshine in January was reached in 2020 with 114.4
hours. This broke the previous record from 2008 (104.3 hours).
In Celtic times, Geneva was a fortified frontier town of the Allobroges against the Helvetii. The place name (58 BC Genava), first attested in Caesar's De bello Gallico, is conventionally attributed to Celtic *genaua ‹mouth› (compare Welsh exactly 'mouth'), similar to Genoa and Arguenon. Since Geneva is not at an estuary but at a drain, it was proposed as an alternative to derive the name from Indo-European *genu-, *gneu- ‹knee, corner, angle›.
Geneva arrived around 120 BC. under the rule of the Romans. During
the Roman Empire it served as a bridgehead, from 400 to 1536 it was a
bishopric. It was also the seat of the Burgundian kings in the fifth and
ninth centuries. In 563, the Tauredunum event, a tsunami in Lake Geneva,
killed many residents.
Since the 10th century, the Bishop of
Geneva has minted his own silver coins. From 1026 Geneva belonged to the
Burgundian part of the Holy Roman Empire, within which it became an
episcopal territory. On August 1, 1034, Conrad II (HRR) celebrated the
acquisition of Burgundy in the Geneva Cathedral. The jurisdiction of the
bishop was circumscribed against the claims of the Count of Geneva in
the deed Placitum de Seyssel of 1124. In 1162 Frederick I granted the
diocese independence and imperial immediacy. In the 13th century, Geneva
became an important trade fair city, which brought more influence to the
urban bourgeoisie. In 1387, the Bishop of Geneva bestowed various
liberties on the city of Geneva, such as citizenship. In 1467 the
Savoyards granted the Genevans freedom of trade on their territory.
Bishop Antoine Champion gathered about 500 priests in the church of St.
Pierre in 1493 and denounced the vicious way of life of the clergy:
«People dedicated to the service of God must be distinguished by a
pure life; but now our priests have surrendered to all vices and lead a
more wicked life than the rest of the flock. Some wear open clothes,
others don warrior helmets, put on red cassocks or cuirasses, go to the
markets, frequent pubs and brothels, behave like comedians or itinerant
actors, take false oaths, lend on pledges and sell shamefully to
perjurers and murderers indulgences."
– Antoine Champion, Bishop of
Geneva, May 7, 1493, quoted in: Jean-Henri Merle d'Aubigné: Of Huguenots
and Mammeluks
In 1526, Geneva joined a league of cities along with Bern and
Fribourg. After convincing sermons by Guillaume Farel, the Reformation
was introduced in 1536 and the independent Republic of Geneva was
proclaimed. Freiburg therefore broke its alliance with Geneva, whereupon
the city tried several times in vain to be admitted to the Swiss
Confederation as a friendly place. Only the evangelical cities of Bern
and Zurich concluded castle rights with Geneva in 1584. The French
reformer Johannes Calvin founded the Geneva Academy in 1559, from which
today's University of Geneva developed. After a failed attempt to raid
the city on a December night in 1602 (Escalade de Genève), Savoy
recognized Geneva's independence in 1603 in the Treaty of Saint-Julien.
From 1540 to 1700, Geneva became an important place of refuge and a new
home for French and Italian Protestant refugees, the Huguenots and
Waldensians. The immigrant families were not only a burden for the city,
but also a social and economic enrichment through their education and
knowledge of silk production and trade and the art of watchmaking, which
they brought with them and settled in Geneva and the surrounding area.
In 1781, the bourgeoisie and the working class gained supremacy,
after which a representative-democratic constitution was adopted, before
the following year, with the help of Bernese-Savoyard troops, the
patriciate seized power again and many industrialists emigrated as
exponents of the bourgeoisie.
On April 15, 1798, Geneva was annexed by France. The unification
treaty of April 26, 1798 regulated the transfer of the Republic of
Geneva to the French state. In August 1798, the city became the capital
of the newly created department of Léman. During the French period, the
civil code was introduced and the city became the administrative center
of the whole region, which also brought economic benefits. However,
troops for the Napoleonic Wars were also levied in Geneva from 1802
onwards.
On December 31, 1813, Geneva was occupied by Austrian
troops. After the independence of the city republic had first been
proclaimed, Geneva asked to be admitted to the Swiss Confederation. On
June 1, 1814, Swiss troops landed in Geneva in accordance with the
decisions of the Congress of Vienna, and on September 12, the Diet
officially confirmed Geneva's admission as the 22nd canton of the
Confederation. The union treaty was signed on May 19, 1815. The city of
Geneva thus became the capital of the newly formed canton of Geneva of
the same name. In a letter dated June 1, 1816, the British writer Mary
Shelley complained about the demolition of the Geneva theater, but the
strictly puritanical Geneva was cosmopolitan and open-minded enough to
found the Musée académique in 1818, which opened two years later at 11
Grand-Rue opened.
French and Sardinian territories were added to
the canton in the Second Peace of Paris (1815) and the Treaty of Turin,
giving the Geneva area a land connection to the rest of Switzerland. In
order not to isolate Geneva economically from its surroundings, several
duty-free zones were successively created around Geneva, which finally
covered almost the entire former area of the Léman department by 1860.
In 1821, the Société genevoise des missions évangéliques was founded on
the model of the Basel Mission. In May 1838 the Grütli Association was
founded in Geneva.
In 1863, the landscape architect
Charles-Guillaume Nitzschner was commissioned to plan the city's
promenades and parks. Geneva became the seat of the International
Committee of the Red Cross in 1864. In the same year, Johann Philipp
Becker founded a German-speaking section of the First International in
Geneva, which held the first congress of the International Working Men's
Association (IAA) in September 1866. The demands of the 25 sections and
eleven cooperating companies were worker protection, the eight-hour day
and the ban on child labor. At the end of the 19th century, the
development of the clock industry benefited from the construction of a
pressurized water network to supply the city with energy and drinking
water. With the Usine des Forces Motrices, which went into operation in
1886, regulation of the water level for Lake Geneva was also introduced.
The increasing energy requirements of industry made it necessary to
build the Usine de Chèvres, which was Europe's largest power plant at
the time. Workers and the bourgeoisie lived in Geneva.
In 1873
Charles II, Duke of Brunswick, left the city a fortune of 1 billion
francs, of which 2 million were used to build the Brunswick Monument.
With a good part of the remaining legacy, she created the Grand Théâtre
de Genève between 1873 and 1879.[36] The largest theater in Switzerland
at the time, designed by Gottfried Semper, had 1,450 seats. The opera
Wilhelm Tell by Giocchino Rossini played at the opening. The demolition
of the city walls under James Fazy from 1849 made room for non-Reformed
places of worship such as those of the Anglican Communion, the Beth
Yaacov Synagogue, or in 1866 the Russian Orthodox Cathedral of the
Exaltation of the Cross. Fyodor Dostoyevsky was among the not a few
Russian guests in Geneva from August 1867 to May 1868, fleeing from his
creditors. The Hôtel des Postes, known as the Poste du Mont-Blanc, was
also built at the base of the city walls in 1890-1892, designed by Marc
Camoletti.
In 1873 the University of Geneva and the
Anti-Authoritarian International were founded. Mikhail Bakunin traveled
to do this. The Russian nobleman and revolutionary was familiar with
Geneva, where he had founded the International Peace League in 1867. In
1896 the second Swiss national exhibition took place with the folkloric
Village Suisse, which brought local culture closer to the people of
Geneva as an exotic attraction and was only surpassed by the
ethnological exhibition of a Village Noir. The Parc de Plaisance offered
a Congolese panorama based on Belgian performances, a Javanese theater,
Arabic music and other amusements. Since 1885, there was a Musée des
Arts Décoratifs in the watchmaking school to meet the need for
decorative arts in the luxury goods industry. Anarchist Luigi Lucheni
stabbed Elisabeth of Austria-Hungary to death in September 1898. In 1895
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov, known as Lenin, came to Geneva for talks with
Georgi Valentinovich Plekhanov.
From 1920 to 1946, Geneva was the seat of the League of Nations,
which Switzerland joined after the referendum of May 19, 1920. The
opening speech of the constituent assembly was given by Federal
President Giuseppe Motta. The League of Nations moved into the Palais
Wilson. From May 4th to 23rd, 1927, the first world economic conference
was held in Geneva. In March 1930, the Lebanese Chakib Arslan founded
the newspaper La Nation arabe in Geneva. From August 16 to 25, 1939, the
21st Zionist Congress took place in Geneva. Geneva became the seat of
the Jewish organization World ORT.
In 1931 the former communes of
Eaux-Vives, Le Petit-Saconnex and Plainpalais were merged with the city
of Geneva. On November 9, 1932 there was a massacre, the so-called
"Bloody Night of Geneva", when soldiers shot 13 anti-fascist
demonstrators and seriously injured 60. In the elections to the cantonal
parliament in November 1933, the extreme right won 9% of the vote.
21st century
Geneva is one of ten Swiss and one of one hundred
European cities that were awarded the honorary title of "European City
of Reformation" by the Community of Protestant Churches in Europe in
2015.
Until 1870, Geneva was the most populous city in Switzerland. The city of Zurich then took over this place, although between 1910 and 1995 the city of Basel also had a larger population. As of December 31, 2020, the city of Geneva had 203,856 inhabitants. The agglomeration of Geneva is redefined every ten years on the occasion of the census and in 2007 had 471,314 inhabitants, or 780,000 inhabitants across the country including France. The proportion of foreigners (registered residents without Swiss citizenship) was 48.3 percent (97,949 residents) on December 31, 2020. This is explained in particular by the number of international organizations in the city and the location near the border with France (the canton of Geneva is almost completely surrounded by France). Geneva's urban area is 15.89 square kilometers. This results in a statistical population density of 12,829 inhabitants per square kilometer (December 31, 2020). The extended metropolitan area, the Geneva-Lausanne metropolitan region, has 1.2 million inhabitants.
Geneva as a financial center
The City Republic of Geneva minted
its own coins until 1850. For a certain time, these were divided into
sols, as was customary in France for a long time, after which francs
were minted.
Industry
Home to luxury watch manufacturers such
as Rolex (headquarters), Omega, Patek Philippe, Vacheron Constantin,
Frédérique Constant or Baume & Mercier, Geneva is one of the most
important watchmaking cities in the world. The quality features
introduced by local crafts such as the Geneva seal (Poinçon de Genève)
and Geneva stripes (Côtes de Genève, filets) are well known. In
addition, numerous multinational companies such as Procter & Gamble and
Ralph Lauren have their (European) headquarters in Geneva. Over 28,000
people work directly for the 30 international organizations based in
Geneva and the 172 accredited missions; the contribution to the economic
output of the canton is 9.2 percent.
Traffic
With the
Genève-Cornavin train station, Geneva is well integrated into the
European rail network. There was also a rail link to Annemasse from the
Gare des Eaux-Vives terminus. The new Genève–Annemasse (CEVA) railway
line, under construction since 1995, has been connecting the Swiss and
French networks since December 15, 2019. Until 2012, Geneva had a
loading point for motorail trains, from 2016 there was no longer any car
transport .
The second largest airport in Switzerland, the
Aéroport International de Genève, is located in the Geneva suburb of
Cointrin.
Geneva lies on the Swiss A1 motorway and the French A40
and A41 motorways.
Local public transport in the city is handled
by Transports publics genevois (TPG), which also operates the Geneva
tramway with four lines and the Geneva trolleybus with six lines.
Furthermore, Geneva is connected to numerous shore towns of Lake Geneva
by passenger shipping on Lake Geneva.
Due to the limited space
and the constant growth of the city, the traffic routes are heavily
overloaded. Along with the housing shortage, mobility is one of the most
pressing issues in the city and canton of Geneva. Attempts to remedy the
impending traffic collapse, for example by building a bridge or a tunnel
to cross the lake, have so far failed, particularly due to the political
disputes between the city and cantonal governments. Alongside Lyon,
Copenhagen and Luxembourg, Geneva is a pilot city for autonomous
minibuses as part of the Horizon 2020 project Autonomous Vehicles to
Evolve to a New Urban Experience (Avenue).
The Hans Wilsdorf
Bridge crosses the Arve.
art trade
In 2006, the Metropolitan
Museum of Art set up a new office in the center of Geneva to serve as a
contact point for collectors and artists. In the Rhone city there are
120 galleries and a bonded warehouse, which is considered the largest
"museum" in the world because of the works of art stored there, but
which is not open to the public.